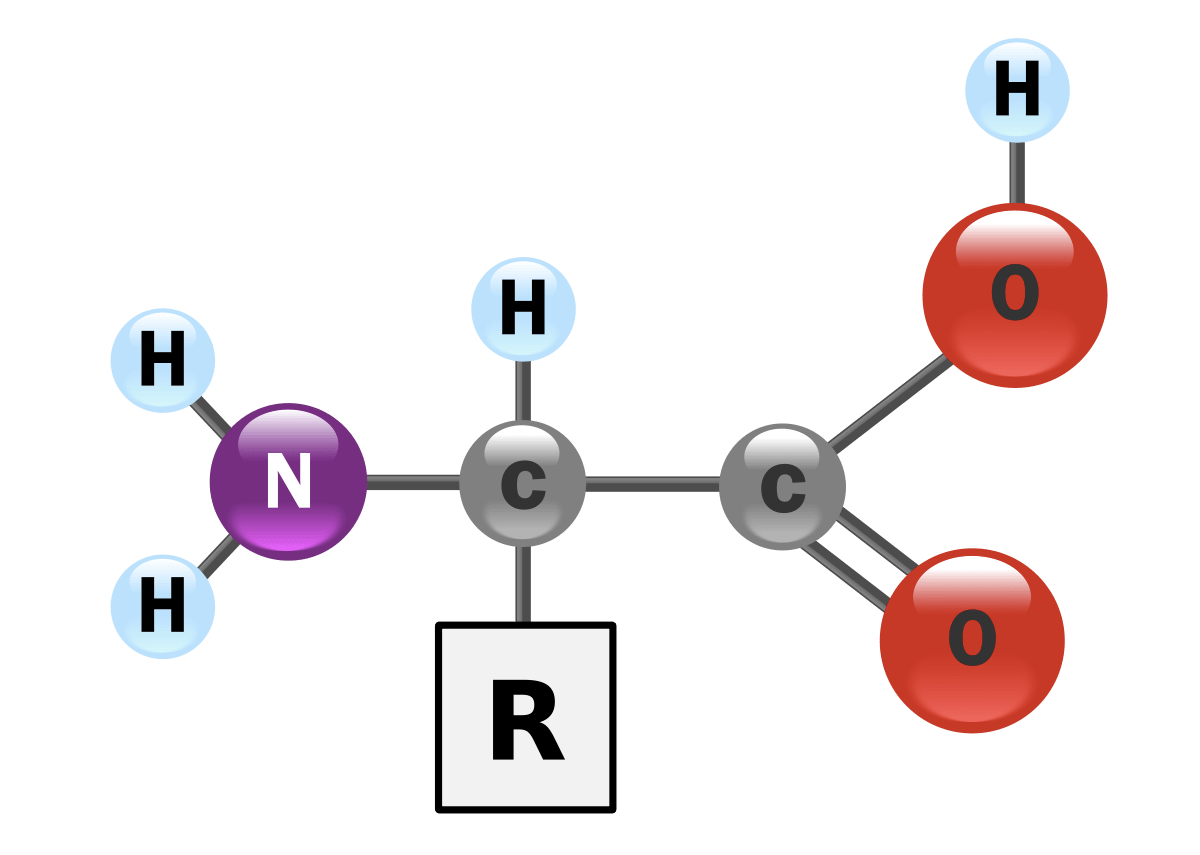
Question 10
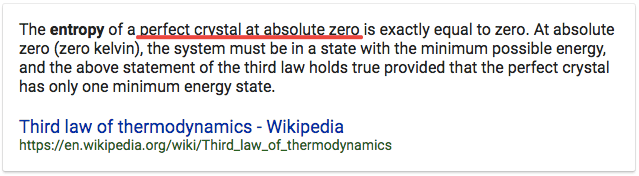
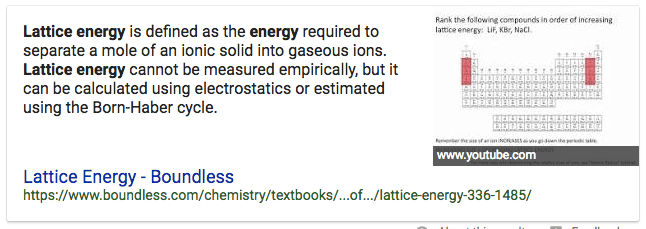
Question 11
Quantity typically determined by measuring the rate of a reaction at two or more different temperatures: Activation Energy
The activation energy can also be found algebraically by substituting two rate constants (k1, k2) and the two corresponding reaction temperatures (T1, T2) into the Arrhenius Equation

Arrhenius Equation
![actvaton energy consänt RT Kelvin temperature the gas consant
frequency factor mathematca\] quantty, e pre-exponenta\] factor](media/image54.png)
Question 49
Most Phosphates are insoluble

Question 54

Raoult's law

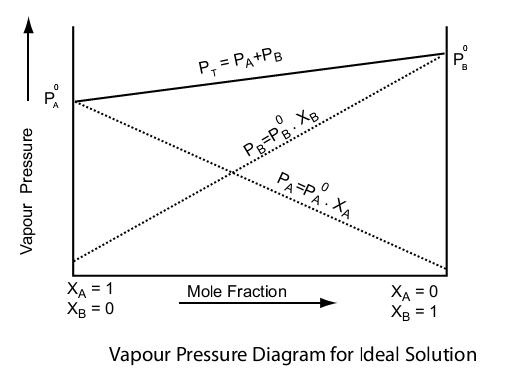
Question 66

Collision Theory
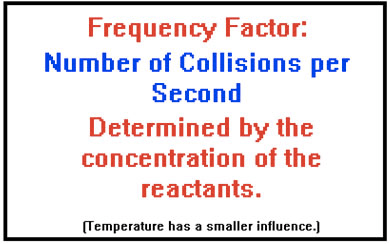
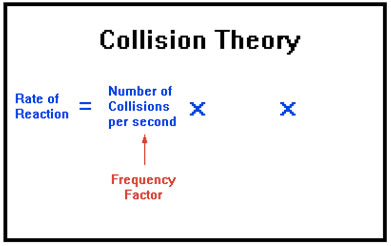
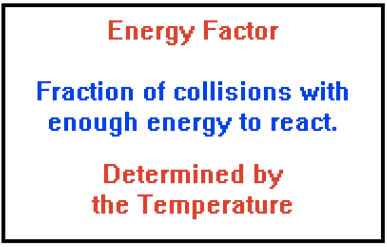
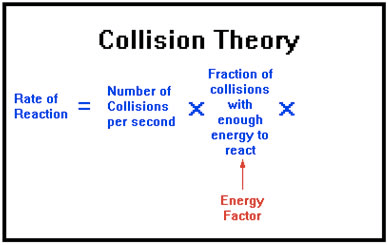
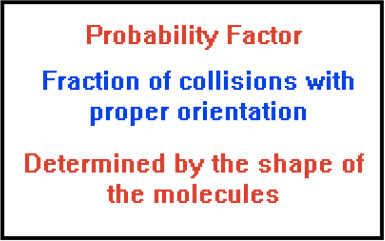
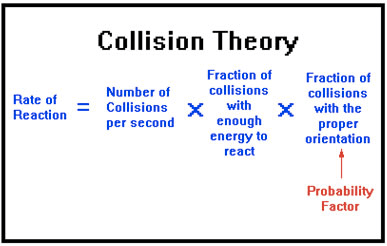
Question 70